Computer networking is a key part of today’s technology. This technology supports sharing of resources and effective communication between computers and devices. Streaming a movie, writing and receiving emails and using cloud services are possible because of networking.
We will look at computer networking here, starting with its definition, the types it has, important components and both the benefits and drawbacks. To help you understand better, I will provide a comparison table.

What is the meaning of Computer Networking?
Computer networking is the strategy of connecting different devices together to communicate and share various kinds of information. Technology utilizes wires or wireless means for these devices to communicate smoothly, thanks to certain protocols.
Classification of Computer Networks
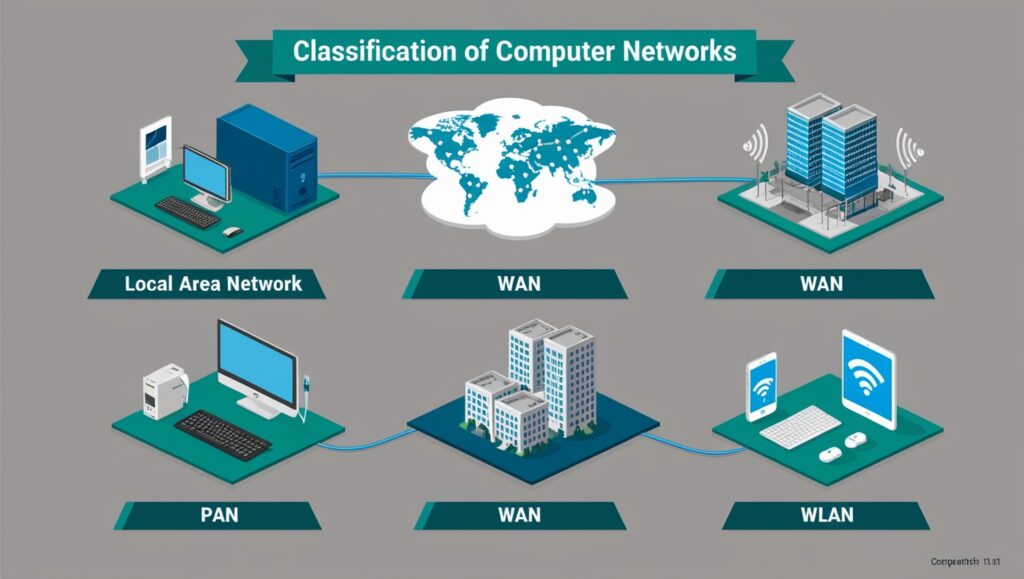
There are several types of computer networks, depending on their scale, the job they perform and the regions they cover. The most important types are:
1. A LAN (Local Area Network)
- Protects only a small location, like a home, an office or a school.
- Data can be transferred very quickly.
- When all the office computers use only one printer.
2. Wide Area Networks are also known as WANs.
- Covers a wide section of the world.
- The slowdown comes from long-distance communication with WAN, unlike with LAN.
- Example: The Internet makes information transfer easy.
3. MAN refers to a Metropolitan Area Network.
- Works across a city or massive campus.
- Much bigger than LAN but still smaller than WAN.
- For example, establish connections between city government offices and buildings.
4. PAN is the acronym for Personal Area Network.
- Short-range network is used for devices close to you.
- For example, Bluetooth is used to connect a phone and a headset.
5. A system built for Wireless LANs is called a WLAN.
- This type of network is like LAN except that it is wireless.
- Is connected through Wi-Fi.
Comparison Table of Different Network Types
| Feature | LAN | WAN | MAN | PAN | WLAN |
| Coverage Area | Small (Office/Home) | Large (Countries) | Medium (City) | Very Small (Room) | Small (Office/Home) |
| Speed | High | Low to Medium | Medium | High | Medium |
| Setup Cost | Low | High | Medium | Very Low | Low |
| Maintenance | Easy | Difficult | Moderate | Very Easy | Easy |
| Example | Office LAN | Internet | City Network | Bluetooth Devices | Wi-Fi Network |
Elements of a Computer Network
- Router: Allows various networks to connect and communicate with each other through data routing.
- Switch: Connects various devices in the same network.
- Modem: Exchange digital and analogy signals to allow your computer to use the Internet.
- NIC (Network Interface Card) is a part of a computer that connects it to a network.
- Wired networks use cables and connectors.
- Access Points: They provide wireless connections.
Network Topologies
The connections among Network nodes are organized by a process called topology.
- Bus Topology: A single cable connects all the network devices.
- In Star Topology, every device is linked to a central hub.
- With Ring Topology, data moves around all of the devices in a ring.
- All devices in a mesh network are linked to every other device.
- Hybrid Topology: A system made by combining different topologies.
Advantages of Computer Networking
| Pros | Explanation |
| Resource Sharing | Allows sharing of files, printers, and internet connections. |
| Centralized Data Management | Data can be stored and managed centrally. |
| Communication | Enables instant messaging, video calls, and emails. |
| Remote Access | Employees can work from anywhere. |
| Scalability | Easy to add new devices without affecting performance. |
| Cost-Efficiency | Reduces hardware costs by sharing resources. |
Disadvantages of Computer Networking
| Cons | Explanation |
| Security Issues | Networks are vulnerable to unauthorized access and cyberattacks. |
| Maintenance Costs | Requires regular maintenance and skilled staff. |
| Complexity | Complex networks need advanced configuration and management. |
| Downtime Risks | A failure in the network can halt operations. |
| Data Loss | Risk of data loss if not backed up properly. |
Popular protocols for different situations
- The Internet depends on TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol).
- HTTP and HTTPS are used to link between servers on the web.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol): To provide file transfer between different computers.
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): This protocol is used when sending emails.
- DNS (Domain Name System) links the domain name to the necessary IP address.
Wired vs Wireless Networks
| Feature | Wired Network | Wireless Network |
| Speed | Generally faster | Usually slower than wired |
| Reliability | High | Can suffer from interference |
| Mobility | Limited | High |
| Installation | Complex (cables required) | Easy (no physical cables) |
| Security | More secure | Vulnerable to hacking |
Examples of Computer Networking

- Data from email can be used in a company through sharing and remote work and by using CRM systems.
- Education: You can take courses online, utilize tools available to you and network with students on campus.
- This area may include sharing medical records online and virtual medical consultations.
- Data is brought together in a single place and there are portals for citizens.
- People use online entertainment such as gaming and constant streaming.
Conclusion
Modern ways of exchanging information and data heavily depend on the structure of computer networking. People and companies can do things such as basic emailing or set up major applications in the enterprise using it. Being aware of the different types, plus their benefits, components and issues helps organizations and individuals choose the best option for their networking.
Improvements in technology will lead to networks that are more connected, speedier and safer. Regardless of whether you work in IT or are simply interested in computers, it’s important to understand computer networking in the modern age. Read more Information about Computer network…















