Over the past few years, Blockchain has shifted from being known in cryptography to becoming a name everywhere from the financial sector to healthcare. With its decentralized and open system, blockchain will likely change how we carry out storing, sharing and verifying information. In this extensive blog post, we study blockchain thoroughly, explain its pros and cons, show examples of where it’s used and compare it in detail to traditional methods.
What is Blockchain?
Data in Blockchain is distributed among all the devices linked in a network which makes it a distributed ledger technology (DLT). Blocks are attached to one another in order to produce a chain. Once a person adds data to these blocks, it cannot be edited or taken back without also updating all the blocks that follow—and this process depends on all members agreeing on the network.
Thanks to the decentralized system, no middle people are needed and everything becomes more transparent and secure. The technology that supports Bitcoin and Ethereum is known as blockchain but has uses in areas other than cryptocurrencies.
working of a blockchain in simple terms.
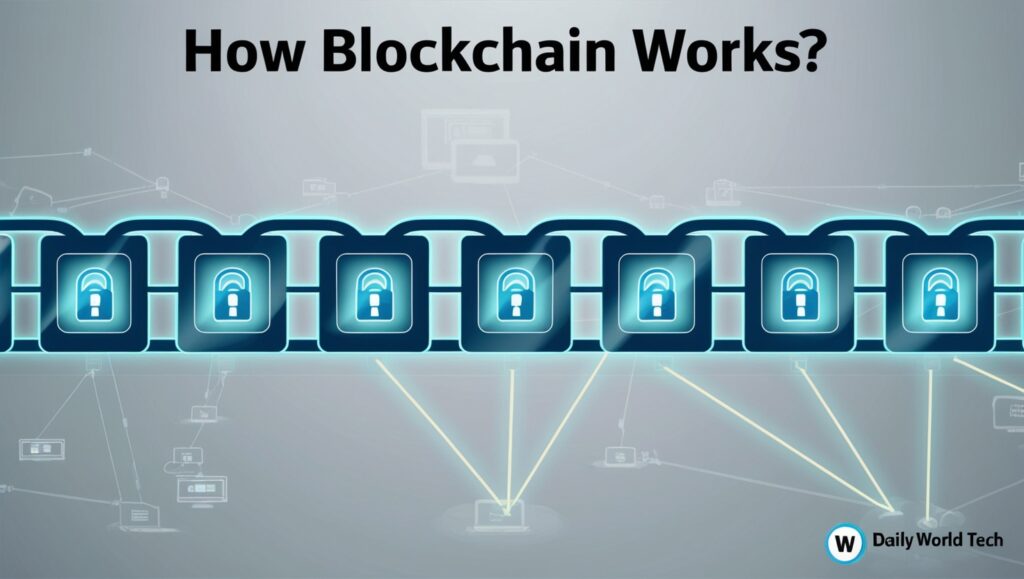
1. When a transaction is made, data is born (is created).
Whenever you send coins, sign an agreement or make an update, a transaction is generated. Examples of this include sending money or storing health data.
2. Transaction Confirmed
Before anything goes on the blockchain, the system ensures the transaction is proper. Since many computers (nodes) use consensus to decide on the status of transactions, decentralization makes it hard for attacks to succeed.
- Proof of Work (PoW): Solving a difficult puzzle of numerical calculations used by Bitcoin.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): means validating transactions using the amount of virtual currency someone possesses.
3. The new Transaction is Added as an Entry in a Block
Once we prove the transaction is valid, it becomes part of a block containing other accepted transactions. A block is a digital page kept in a digital ledger.
4. The Block has a Link to the Blockchain
The link between two blocks is formed when a hash, a special kind of code, is assigned to the new block. That’s why it’s called a blockchain: an ongoing series of interconnected blocks. There are:
- Block has its own information.
- The unique identifying digital fingerprint
- A hash is generated from the previous block’s data.
This connection makes the blockchain safe. Attempting to modify a block will result in its hash changing and then breaking the chain.
5. Updates are made to the Blockchain and then shared with others.
The entire blockchain is updated on all devices part of the network after a block is added. Because each person sees the same ledger, there is transparency and trust in the system.
Result: The records are protected, transparent and cannot be changed without being noticed.
- If you want to change data, you have to alter every block that comes after it.
- No one government manages the system.
- Hashes and validation from the community ensure that blockchain is safe.
Important Aspects of Blockchain
- Decentralization: Everyone holds a part of the data.
- All participants of the system have the ability to observe the ledger.
- Once data is stored, it remains unchangeable.
- Methods such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) are used to bring agree knowns among people running the network.
- Smart Contracts: Programs that automatically execute an agreement once the rules are followed.
Pros and Cons of Blockchain
| Pros | Cons |
| Enhanced security | High energy consumption (especially PoW) |
| Greater transparency | Scalability issues |
| Reduced costs (no intermediaries) | Complexity and lack of standardization |
| Improved traceability | Irreversible transactions |
| Faster transaction times (in some cases) | Regulatory uncertainty |
Blockchain vs. Traditional Databases
| Feature | Blockchain | Traditional Databases |
| Structure | Decentralized ledger | Centralized |
| Data Immutability | Immutable | Mutable |
| Security | High (cryptographic) | Varies, often lower |
| Transparency | High (publicly viewable) | Limited to admins or authorized users |
| Cost of Maintenance | Potentially lower (no intermediaries) | Higher (infrastructure and manpower) |
| Speed | Slower (due to consensus mechanisms) | Generally faster |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, etc. | Banking, CRM, ERP, websites, etc. |
Blockchain Technology’s Useful Applications
- Finance and Banking: Thanks to blockchain, fraud is decreased, transactions happen faster and costs are reduced.
- Through Supply Chain Management, businesses can follow and confirm the movement of goods live.
- Shares patient data securely in healthcare.
- Voting Systems: Makes voting fair and safe so nobody can change the vote.
- Real Estate: Makes it easier to buy and sell using digital identities and smart contracts.
- Decentralized digital IDs are being used to make authentication safer.
- Intellectual Property gives people legal ownership over their works and digital materials.
There are different forms of Blockchain.
- Public Blockchain is available for everyone to use (a good example is Bitcoin and Ethereum).
- In contrast, Private Blockchain only allows a small group with permission to take part.
- Consortium Blockchain runs under the management of several organizations.
- It combines both public and private blockchains.
The Struggles in Blockchain
- Federal and state governments are still creating legislation for crypto.
- PoW technologies like Bitcoin involve a lot of energy usage.
- The network may become too busy which results in delays.
- Linking to Outdated Systems: There are few options for linking these systems.
- In today’s world, most people find it hard to learn.
What Blockchain Will Become

With the advancing maturity of blockchain, it should become both more sustainable, scalable and user-friendly. As AI and IoT are more connected and laws become clearer, a larger number of companies will adopt it. Blockchain is thought by some to be as ground-breaking as the internet, changing a wide range of industries.
Conclusion
Blockchain is useful for more than cryptocurrencies; it also introduces a new way to store data, ensure transparency and earn trust. Despite the difficulties, the many benefits indicate that this area should still be developed further. Blockchain is on the way to revolutionizing our interactions with online systems and people.
With the knowledge of blockchain’s main ideas, pros and cons, everyone can choose whether or not to use it. Read more about Blockchain.















