The world of telecommunications is in a continuous revolution, and a technological innovation that can be described as a disruptive technology is the 5G technology that promises to revolutionize the industries, economies, and human lives through experiences. Like the predecessors 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G, 5G is not just an update but does mark a new era of connectivity with ultra-high speed, lower latency, and higher connectivity as well as the ability to support the next generation of digital gadgets and smart systems.
What is 5G Technology?
5G is the abbreviation of the fifth generation of wireless communication networks. Whilst its predecessors were mostly aimed at driving data transmission speeds higher, 5G has a lot more in store than that. It also comes with huge advancements in bandwidth, latency, reliability, and the device-count it can accommodate concurrently.
Although 4G was used to watch HD video content and play online games, 5G will be used to connect various things (self-driving cars, smart cities, and even telemedicine). It runs over a wider range of radio frequencies and uses innovative technologies that include Massive MIMO, beamforming, or network slicing.
How Does 5G Technology Work?
The 5G technology operates through the network design, newly found methods of communication, and advanced radio frequencies to provide more reliable, faster, and low-latency wireless communication. The following are how it works:
1. Radio Frequencies (Spectrum)
There are three frequencies, which are used to transfer data via 5G:
- Medium/Low Band Spectrum (below 1 GHz):
Wider coverage due to long distances achieved, which have slower speeds. Rural areas are good. - Mid-Band Spectrum (1–6 GHz):
Even reporting and swiftness. Cities and towns are ideal. - High-Band Spectrum (24 GHz and more – mmWave):
Tremendous fast speeds and minimal latency, poor range. Suitable for crowded cities.
2. Massive MIMO and Small Cells
- Small Cells:
The 5G uses small cell towers installed closely (several hundred meters apart). These mini towers eliminate the traffic rush and ensure high speeds in data transmission. - Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output):
To increase capacity and reliability, 5G communicates numerous signals simultaneously using numerous antennas on towers and phones.
3. Beamforming
The method assists in narrowing down the signal in one direction rather than bombarding it in modern directions. It enhances signal reception and minimizes the interference, particularly in crowded areas.
4. Network Slicing
The 5G networks have the capability to be split into what is called a slice which is uniquely optimized for various tasks:
- One slice to emergency services with ultra-reliability.
- Another to be used by consumers on their mobile.
- An industrial automation or a gaming slice.
5. Edge Computing
Rather than transmit all the information to distant data facilities, edge computing in 5G enables the information to be processed nearer to the user (at the network edge). This decreases delay (latency) and enhances real-time responsiveness, which is essential to such things as self-driving cars and VR.
6. High Speed, Low Latency
- Latency: 5G limits latency to just 1 millisecond, which is perfect in real-time applications.
- Speed: It provides download speed of up to 10 Gbps enabling stream of HD video and downloading of files instantly along with providing high-performance gaming.
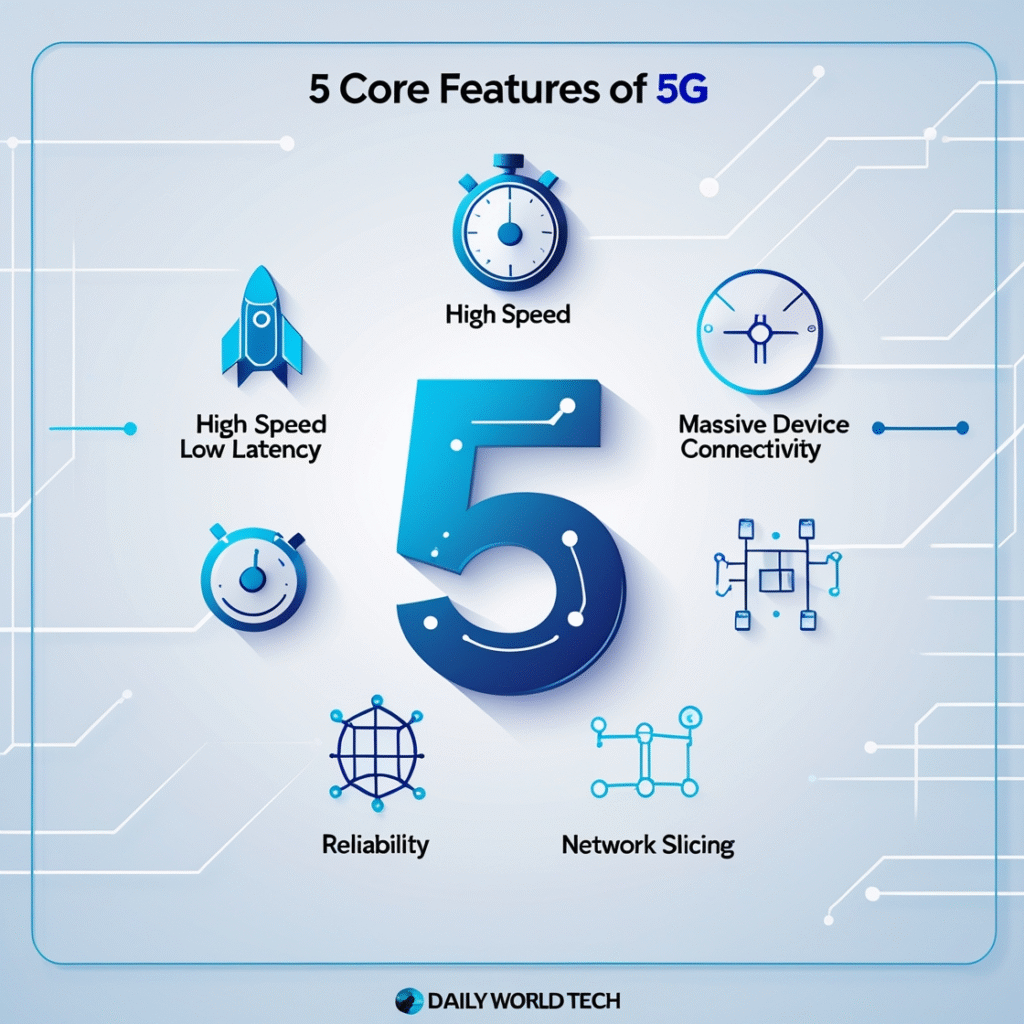
Key Features of 5G
1. High Speed
The 5G networks achieve a faster rate of up to 10 Gbps—approximately 100 times more than 4G. This will facilitate the downloading of high-definition movies within seconds, providing the possibility of easy streaming of movies and game execution on clouds and real-time transfer of data in the cloud.
2. Ultra-Low Latency
Latency defines the time lag between sending and receiving data. 5G creates a total disruption in the latency of only 1 millisecond (ms), which is much lower than 50 ms of 4G. It is crucial to such uses as autonomous vehicles, robotics, and augmented reality (AR).
3. Enormous Machine Connectivity
5G is designed to hold up to 1 million devices per square kilometer, therefore, the Internet of Things (IoT) is ideal. Wearable technology, connected automobiles, smart cities, and smart homes will all be possible in a 5G network.
4. Better Reliability and Efficiency
5G promises increased network availability, improved energy consumption of a product, and facilitation of mission-critical applications, including emergency response systems and medical tools.
5. Network Slicing
This is an innovative capability that enables allotment of virtual networks in one physical 5G network. As an example, there could be a slice of the network specific to hospitals, another one dedicated to factories, and another one dedicated to users.
Uses of 5G Technology
The transitional aspect of the 5G is the extensive use in all sectors. Some of the critical areas where 5G is going to have a tremendous impact include the following ones:
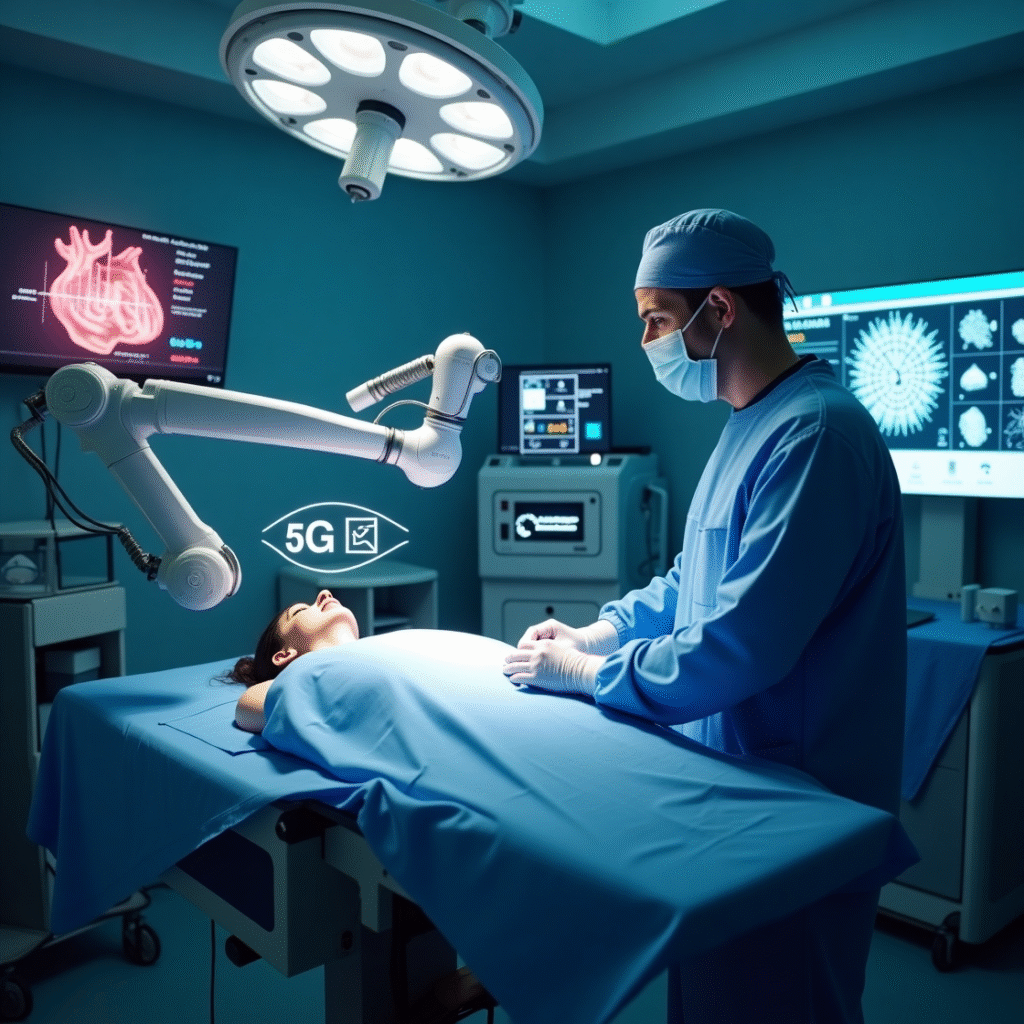
1. Healthcare
With 5G, real-time remote diagnostics, robot-assisted surgeries, and connected medical devices become a possibility. A doctor in one country can operate a patient in another with the help of robotic limbs operated by the ultra-low-latency 5G infrastructure.
2. Transportation
Self-driving cars will have to communicate with high speeds between itself and other cars on the road, and the infrastructure. 5G will provide instant communication when it comes to avoiding collisions, traffic control, and navigation. Vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) systems as well as smart traffic lights are not left out.
3. Industry 4.0 – Manufacturing and Industry Competency
5G is used in smart factories to hold together manufactured systems, robots, and sensors. It results in real-time tracking, preventive maintenance, automatization, and productivity. The digital twin—that is, the maintenance of a virtual representation of a factory on a real-time basis—becomes possible using 5G.
4. Entertainment and Media
5G introduces a whole new level of consuming media: whether it is 4K/8K streaming, augmented reality (AR) or virtual reality (VR) experiences, everything is possible. The 5G speed and reduced latency rates take all the good advantages of cloud-based gaming such as Google Stadia or the Xbox Cloud.
5. Education
5G also transforms the education sector, as it allows immersive distance learning that is configured by VR, AR, and video conferencing using high-definition video feed. Virtual interaction in the virtual classrooms is smooth.
6. Agriculture
With 5G, smart farming would be more effective. Farmers will be able to survey crops with drones, sensors will be able to measure soil and weather, as well as machinery being remotely controlled to become more efficient and cut down on waste.
7. Smart Cities
Ranging between smart lighting, waste management of the city, surveillance, and emergency services, 5G can assist infrastructures being built to enhance the urban experience. SIR ensures safer cities are created because the process involves real-time data collection and response mechanisms making cities cleaner and efficient.
Advantages of 5G Technology
1. Optimized User Experience
The connection speed is up to 10 Gbps and latency is almost zero, which means that you may instantly download, stream with no buffers, and play web-based games.
2. Economic Growth
In different economic projections, 5G will amass trillions of dollars of economic value in the global economy in the coming decade. It creates fresh markets and innovation in directorates.
3. Job Creation
The new possibilities associated with 5G will emerge in the spheres of engineering, cybersecurity and AI, cloud computing, and IoT-related services, requiring massive increasing numbers of qualified personnel.
4. Patronage of the Emerging Technologies
Fast and efficient networks are the pillars of technologies such as AI, blockchain, VR/AR, big data, and edge computing which are the foundation of this innovation.
5. Environmental Benefits
One way through which 5G can help in sustainability is through energy consumption, decrease in emissions, smart grids, and accurate agriculture with limited chemical applications.
Issues and Worries
In spite of all the mentioned benefits, the introduction and implementation of 5G work with a number of challenges:
1. Infrastructure Requirements
5G needs a high concentration of small cells, fiber-optic, and base stations. Development of this infrastructure, more so in the rural settings, is expensive and time-consuming.
2. Spectrum Allocation
Governments should free up high-frequency spectrums of 5G. Deployment may be delayed due to the short supply of these spectrums and competition in the telecom’s provider network.
3. Security, Privacy
As more and more devices are connected to a 5G network, there is an increased chance of a cyber-attack and data breach. Network providers should install sound security measures.
4. Health Concerns
There has been an uproar concerning possible health hazards because of the sources of high radiations by 5G antennas. But up to now, these claims have not been backed with hard scientific findings.
5. Adoption Cost
The services and equipment in 5G would be costly, becoming unattainable in low-income neighborhoods or in developing countries at the outset.
Global Rollout of 5G
The world nations stand at a different position in terms of the deployment of the 5G:
- United States: Verizon, AT&T, and T-Mobile are critical telecom operators that have already deployed 5G in several cities and intend to expand to the rest of the country.
- China: China is the leader of 5G infrastructure having hundreds and thousands of base stations and commercial coverage.
- South Korea: It is one of the earliest to adopt 5G and its usage is high in Seoul and other cities.
- Europe: Countries such as Germany, UK, and France are mixed in launching 5G at different speed and geographical coverage.
- Pakistan and Developing Countries: There is still early stages involved but governments and other telecom operators are engaged in preparing pilots and dispensing spectrum licensing.
Future of 5G
1. Alliance – 6G
Although 5G technology is currently only in its early stages of adoption, the work on 6G is already being done. It is supposed to take advantage of the strengths of 5G and add newer features, like terahertz communication and AI-native networking, and even less latency.
2. Universal IoT Ecosystems
Houses, cars, workplaces, and even human bodies (through health monitors) will join interconnected IP-based extended systems, and 5G will be the thread that ties this huge net of smart things together.
3. Edge Computing
5G will spur edge computing, where regional data are subjected to computation and processing at the edge rather than routes to centralized cloud servers. This minimizes latency and increases security.
4. Robotization and Artificial Intelligence
The ability of faster data processing that such 5G networks will necessitate will be necessary in automation of industries such as logistics, finance, and customer service as they require the ability to make real-time AI decisions.
5. Rural Inclusion
Telemedicine, e-learning, and agricultural technologies will be made available to rural people as the infrastructure is extended, and the digital divide will be closed.















